Thelenberg 2012 13
Inhaltsverzeichnis
|
KLAUSUR
- Klausur besteht aus listening + questions on a text
- Look into the wiki!
1. BRAVE NEW WORLD ist nicht Klausurstoff!
2. Foreign Policy:
Aus diesem Bereich wird auch diie Listening Comprehension sein!
Wiki: 4 US Foreign Policy and Relations to Europe, incl. Worksheets, Buchtexten, Voc
Texts:
- American cultural hegemony and Anti-Americanism
- The USA and Europe – too different to be friends?
- What do Americans think of Europe
- Greenline p. 60/61 Brand Aid
- Greenline p. 82/83 America is a Religion
- Worksheet on US-Wars
- The Home Front: Exorcising an old Demon
Video:
Read:
3. Robots / Science:
Wiki: 5. Science and Technology incl. Worksheets, Listening Comprehension
Texts:
- Programmed for Love
- Nicht Text: Barney
Homework
Look at the collection of aspects of the drama on this page!
- What elements are used in films too?
- What additional/different possibilities does a film have + what does this mean for the audience?
Recent homework
Basic Skills & Information
- Information on homework and oral grades
- Reading and Marking technique - SQ3R Method A useful method to read, mark and annotate texts.
- Working with Cartoons
- A good speech/speaker ...
- Answering questions on the text
- Starting a paragraph
- Starting an Essay/Comment
- Writing an interview
- Mediation
- Characterization
- Building an Argument
Brave New World
Brave New World is a separate page now! Open here!
US Foreign Policy and Relations to Europe
Typically American? A collection of Stereotypes?
| Typical Americans are .... / Typically, in America you find ... / In America "they" believe in ... |
|---|
|
Cartoons on US Cultural Hgemony / Americanization
- Cartoon on Americanization
- Cartoon of President George W. Bush as Cowboy
- Working with Cartoons
- Notes on Cartoon!
Text on US Cultural Hegemony
1. What reasons for anti American feelings in Europe does the text give?
- American culture ousts European culture
- German or other European languages are being flooded with English terms and expressions
- Sense of national identity severely disturbed
- Europeans are afraid of loosing their cultural autonomy
- European culture replaced by American culture
- Vietnam-war
- Guantanamo Bay and Abu-Ghraib
- Americans ignore and don't know about European culture
- American worldview is centered on America
- Americans expect everyone to think and speak American
- Americanization as cultural imperialism
2. Why has Germany been especially quick at embracing American culture?
- America's help after WWII (→ Marshall Plan) ==> Germans felt grateful
- German culture discredited by Nazis, German from "Dichter und Denker" to "Richter und Henker"
- Germans looked for new cultural model → culture of the victoriuos, democratic and successful USA
- Germans were not allowed to have and learned to feel ashamed of patriotic feelings → easy to take over Western/US mass culture
- US culture meant luxury, affluence, freedom, individualism
The USA and Europe - increasingly difficult relations?
The results of your work on the two texts on the relations between the USA and Europe:
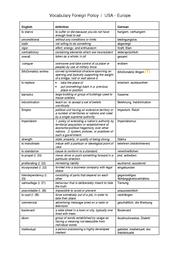
Vocabulary
Text: Brand Aid
- Cf. Greenline p. 60/61
- Click several times to enlarge!
The Wars of the USA in the 20th and 21st century
- Cf. worksheet on Wars
- Your summaries of the wars:
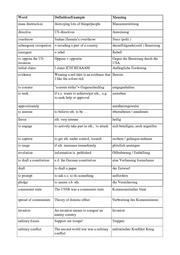
Vocabulary
The Home Front: Exorcising an old Demon
- Cf. workshhet, or partly here (p. 267/268):
- Comparison Vietnam War and Gulf War:
Science and Technology
Listening Test
Using Robots
Text: Programmed for Love
- The original text can be read here!
- Answers to questions 1 and 2 (click several times!):
Drama, Baby, Drama
From Poetry to Drama
Watch the difference between poetry and drama:
To turn the recital of a poem into "drama" one must ...
- put emotion in by varying the level of your voice
- vary your speed, speak in a shivering/slow/tired voice
- use gestures and facial expressions
- introduce music to support the mood e.g. slow instrumental
- several actors, representing the victims and the police. The victims are taken away one after the other. One person recites the poem.
- interaction between characters e.g. others passivly watch
- costumes e.g. for the soldiers, police
- images as background
- use a chorus, which speaks certain passages together
- don't do any of these to keep it minimalistic
- use lighting e.g. spot on one actor
.
Voice and the characters' interaction change everything!
... or can at least almost completely change the effect of the same line.
- Compare these examples!
- Practice this sentence with a partner (Take turns, play at least two different versions, the silent partner uses gesture/facial expressions)!
- I don't know what what she's up to. I just want to say "Good-bye".
- What is the general situation? (When, where does this happen?)
- What is the relation between the two characters (Who are they?)
- What do the characters want to express? (verbally and non-verbally)
Drama - a Definition
Drama is the specific mode of fiction represented in performance. The term comes from a Greek word meaning "action" (Classical Greek: δρᾶμα, drama), which is derived from "to do" (Classical Greek: δράω, drao). The enactment of drama in theatre, performed by actors on a stage before an audience, presupposes collaborative modes of production and a collective form of reception. The structure of dramatic texts is directly influenced by this collaborative production and collective reception. From http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drama
Drama - Identify main aspects and elements
Look at the following webpages and try to sum up/note down the main aspects of drama. Do not use the video examples yet!
Write your answers into your groups section
- Do not just copy and paste!
- Try to shorten and condense!
- If there are no examples e.g. for the effect of a certain element - find simple ones!
- Try to clearly work out what possibilities/effects a certain element/aspect of drama has!
Elements of Drama - as a literary Genre -(Pages 1,3,4)
BBC GCSE Revision on Elements of Drama
- (Do not use page 2 of this set)
Elements of Drama- as a literary Genre(Pages 5-7)
BBC GCSE Revision on Elements of Drama
Irony See esp. Dramatic Irony
Aspects of Drama as medium-(Pages 1-3)
BBC GCSE Revision on Drama - Medium I
Aspects of Drama as a medium-(pages 4-6)
BBC GCSE Revision on Drama - Medium II
Space and levels:
- acting area is called „stage“
- how it is used is affected by the drama you are going to play
- levels (Ebenen): visually more interesting, more opportunity for actors, levels may represent different places, audience see parts more clearly
Movement, mime, gesture
- Movement → characterization, feelings, etc. , e.g. (jumping, hyperactive movements, hesitate), must fit character
- Mime → physical theatre (without words), which also uses mime techniques, and where actors can also mime items of set or props
- facial expression (dt.: Mimik!) → expresses feelings, can be combined with gestures/language
- Gesture → arm/ leg movements, bow one’s head → body language
Sets and Props
- stage sets (Bühnenbild): create the backgrounds; best: simple
- props (Requisiten): items which are held or used by actors (need lot of experience, because they can slow down action; effect: characterize s.o, more demonstrative, needed for the action)
Aspects of Drama as a medium - (pages 7-8)
BBC GCSE Revision on Drama - Medium III
Voice:
- tone: appropriate to person/situation (e.g. old person, aggression, you are sad …)
- volume: loudness (stress words, shout, whisper)
- pitch (high/low → feelings)
- clarity: use clear speech - or mumble, if it helps to characterize the person you play
- pace: not too fast / very slow (insecure?); vary speed°!
Spoken Language:
- Language registers: depend on the person you speak to (social status, children, foreigner etc.)
- verse: stylised speech
- Shakespearean language: to reflect Shakespearean times
- slang: to reflect down-to-earth daily life