Thelenberg 2012 13
Inhaltsverzeichnis
|
KLAUSUR
- Klausur besteht aus listening + questions on a text
- Look into the wiki!
1. BRAVE NEW WORLD ist nicht Klausurstoff!
2. Foreign Policy:
Aus diesem Bereich wird auch diie Listening Comprehension sein!
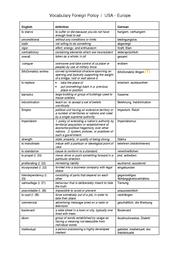
Wiki: 4 US Foreign Policy and Relations to Europe, incl. Worksheets, Buchtexten, Voc
Texts:
- American cultural hegemony and Anti-Americanism
- The USA and Europe – too different to be friends?
- What do Americans think of Europe
- Greenline p. 60/61 Brand Aid
- Greenline p. 82/83 America is a Religion
- Worksheet on US-Wars
- The Home Front: Exorcising an old Demon
Video:
Read:
3. Robots / Science:
Wiki: 5. Science and Technology incl. Worksheets, Listening Comprehension
Texts:
- Programmed for Love
- Nicht Text: Barney
Homework
Look at the collection of aspects of the drama on this page!
- What elements are used in films too?
- What additional/different possibilities does a film have + what does this mean for the audience?
Recent homework
Basic Skills & Information
- Information on homework and oral grades
- Reading and Marking technique - SQ3R Method A useful method to read, mark and annotate texts.
- Working with Cartoons
- A good speech/speaker ...
- Answering questions on the text
- Starting a paragraph
- Starting an Essay/Comment
- Writing an interview
- Mediation
- Characterization
- Building an Argument
Brave New World
Brave New World is a separate page now! Open here!
US Foreign Policy and Relations to Europe
Typically American? A collection of Stereotypes?
| Typical Americans are .... / Typically, in America you find ... / In America "they" believe in ... |
|---|
|
Cartoons on US Cultural Hgemony / Americanization
- Cartoon on Americanization
- Cartoon of President George W. Bush as Cowboy
- Working with Cartoons
- Notes on Cartoon!
Text on US Cultural Hegemony
1. What reasons for anti American feelings in Europe does the text give?
- American culture ousts European culture
- German or other European languages are being flooded with English terms and expressions
- Sense of national identity severely disturbed
- Europeans are afraid of loosing their cultural autonomy
- European culture replaced by American culture
- Vietnam-war
- Guantanamo Bay and Abu-Ghraib
- Americans ignore and don't know about European culture
- American worldview is centered on America
- Americans expect everyone to think and speak American
- Americanization as cultural imperialism
2. Why has Germany been especially quick at embracing American culture?
- America's help after WWII (→ Marshall Plan) ==> Germans felt grateful
- German culture discredited by Nazis, German from "Dichter und Denker" to "Richter und Henker"
- Germans looked for new cultural model → culture of the victoriuos, democratic and successful USA
- Germans were not allowed to have and learned to feel ashamed of patriotic feelings → easy to take over Western/US mass culture
- US culture meant luxury, affluence, freedom, individualism
The USA and Europe - increasingly difficult relations?
The results of your work on the two texts on the relations between the USA and Europe:
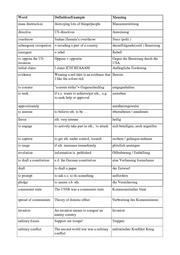
Vocabulary
Text: Brand Aid
- Cf. Greenline p. 60/61
- Click several times to enlarge!
The Wars of the USA in the 20th and 21st century
- Cf. worksheet on Wars
- Your summaries of the wars:
Vocabulary
The Home Front: Exorcising an old Demon
- Cf. workshhet, or partly here (p. 267/268):
- Comparison Vietnam War and Gulf War:
Science and Technology
Listening Test
Using Robots
Text: Programmed for Love
- The original text can be read here!
- Answers to questions 1 and 2 (click several times!):
Drama, Baby, Drama
From Poetry to Drama
Watch the difference between poetry and drama:
To turn the recital of a poem into "drama" one must ...
- put emotion in by varying the level of your voice
- vary your speed, speak in a shivering/slow/tired voice
- use gestures and facial expressions
- introduce music to support the mood e.g. slow instrumental
- several actors, representing the victims and the police. The victims are taken away one after the other. One person recites the poem.
- interaction between characters e.g. others passivly watch
- costumes e.g. for the soldiers, police
- images as background
- use a chorus, which speaks certain passages together
- don't do any of these to keep it minimalistic
- use lighting e.g. spot on one actor
.
Voice and the characters' interaction change everything!
... or can at least almost completely change the effect of the same line.
- Compare these examples!
- Practice this sentence with a partner (Take turns, play at least two different versions, the silent partner uses gesture/facial expressions)!
- I don't know what what she's up to. I just want to say "Good-bye".
- What is the general situation? (When, where does this happen?)
- What is the relation between the two characters (Who are they?)
- What do the characters want to express? (verbally and non-verbally)
Drama - a Definition
Drama is the specific mode of fiction represented in performance. The term comes from a Greek word meaning "action" (Classical Greek: δρᾶμα, drama), which is derived from "to do" (Classical Greek: δράω, drao). The enactment of drama in theatre, performed by actors on a stage before an audience, presupposes collaborative modes of production and a collective form of reception. The structure of dramatic texts is directly influenced by this collaborative production and collective reception. From http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drama
Drama - Identify main aspects and elements
Look at the following webpages and try to sum up/note down the main aspects of drama. Do not use the video examples yet!
Write your answers into your groups section
- Do not just copy and paste!
- Try to shorten and condense!
- If there are no examples e.g. for the effect of a certain element - find simple ones!
- Try to clearly work out what possibilities/effects a certain element/aspect of drama has!
Elements of Drama - as a literary Genre - (pages 1,3,4)
BBC GCSE Revision on Elements of Drama
- (Do not use page 2 of this set)
Plot, action and content
- The plot of the drama is shown in the 'through-line' of the drama - its beginning, middle and end, the arrangement of the scenes - although it doesn't have to be presented in a linear structure. The characters in a play are also part of the plot.
- The action of the drama consists in the events that the characters take part in as they act the play.
- The content of the drama lies in the themes it deals with, eg bullying, the responsibilities of power, the bravery of ordinary people etc.
Climax/anti-climax
- Climax / anti-climax → expectation in the audience → intent → relieved when things turn out well
Contrast
- Contrasts are used in dramas to focus the audience’s attention. They bring the drama to life and make it interesting.
- Example: In a courtroom drama: At first there's the hectical actionof bringing in the prisoner, with everyone scurrying around trying to see and hear the judge's pronouncement. Then there's the sound of the gavel banging on the judge's desk - and the resulting quiet before he pronounces the sentence. The audience can't fail to be interested!
Elements of drama- as a literary genre(pages 5-7)
BBC GCSE Revision on Elements of Drama
Characterization:
- the way they walk and move (body language)
- the way they speak (vocal qualities)
- their reaction to events in the drama
- the way you present the character
Dramatic conventions: techniques for dramatic effects:
- slow motion
- freeze-frame (the picture standing)
- audience aside
- soliloquy (monoloque)
- using one part of the stage as one location, and a different part as another location
Possible symbols (=standing for "real things") for making the drama more believable:
- props (eg a torn wedding photograph to represent a divorce)
- gestures (eg finger on lips as a symbol of silence)
- expressions (eg open mouth to represent surprise)
- costume (a white costume as a symbol of innocence, purity, death, or lack of emotion))
- lighting (eg blue lighting to represent night-time)
- setting (dry ice vapour to represent a snowy wood; a mountain top → loneliness)
Irony
See esp. Dramatic Irony
Aspects of Drama as medium -(pages 1-3)
BBC GCSE Revision on Drama - Medium I 1. Costume, masks and make-up
- costumes give the characters extra features
- masks express non-human characters
- make-up "ages" actors or indicates fantasy characters
2. Sounds and music
- add atmosphere
- emphasize action happening on stage
- help set the scene
- indicate a change of time or location
- focus attention on to a character
3. Lighting
- Spot: one character is stressed
- Fresnel: soft overall light
- Flood: clear wide-angled light
- colour filters can be used for the last three ones.
- Strobe: flashing lights used for special effects.
Aspects of Drama as a medium-(pages 4-6)
BBC GCSE Revision on Drama - Medium II
Space and levels:
- acting area is called „stage“
- how it is used is affected by the drama you are going to play
- levels (Ebenen): visually more interesting, more opportunity for actors, levels may represent different places, audience see parts more clearly
Movement, mime, gesture
- Movement → characterization, feelings, etc. , e.g. (jumping, hyperactive movements, hesitate), must fit character
- Mime → physical theatre (without words), which also uses mime techniques, and where actors can also mime items of set or props
- facial expression (dt.: Mimik!) → expresses feelings, can be combined with gestures/language
- Gesture → arm/ leg movements, bow one’s head → body language
Sets and Props
- stage sets (Bühnenbild): create the backgrounds; best: simple
- props (Requisiten): items which are held or used by actors (need lot of experience, because they can slow down action; effect: characterize s.o, more demonstrative, needed for the action)
Aspects of Drama as a medium - (pages 7-8)
BBC GCSE Revision on Drama - Medium III
Voice:
- tone: appropriate to person/situation (e.g. old person, aggression, you are sad …)
- volume: loudness (stress words, shout, whisper)
- pitch (high/low → feelings)
- clarity: use clear speech - or mumble, if it helps to characterize the person you play
- pace: not too fast / very slow (insecure?); vary speed°!
Spoken Language:
- Language registers: depend on the person you speak to (social status, children, foreigner etc.)
- verse: stylised speech
- Shakespearean language: to reflect Shakespearean times
- slang: to reflect down-to-earth daily life
Grammar
If-Clauses
Related Tenses that you need do know:
- Simple Present: infinitive (+s) ⇒ I go, he runs
- Will-Future: will + infinitive ⇒ we will meet
- Simple Past: infinitive + ed or irregular past ⇒ they talked / you came
- Past Perfect: had + past participle (3rd form of verb) ⇒ he had seen, you had asked
- Conditional I: would/could/should/might + infinitive ⇒ I would help you, we could travel
- Conditional II:
http://www.ego4u.de/de/cram-up/grammar/conditional-sentences/type-1
Explanations and exercises: