Thelenberg 2011 12: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
K (→Videos) |
K (→Cartoon) |
||
| Zeile 438: | Zeile 438: | ||
[https://thebaochi.files.wordpress.com/2011/10/cartoon.jpg Cartoon women's rights in Islamic countries] | [https://thebaochi.files.wordpress.com/2011/10/cartoon.jpg Cartoon women's rights in Islamic countries] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Version vom 19. Oktober 2017, 18:53 Uhr
Homework
Prepare one of the two dialogues on in the "box" on the right at the top of the page!
- Prepare to be candidate A or B!
- Think about how you would start the dialogue!
Recent Homework
Describe and comment on this cartoon! (3 minutes!)
Write a review on the play "The Incident" until Wednesday June 8!
It should be between 400 and 600 words long!
Follow the guidelines here
Read the script of "An Incident" from page 47 to page 51, l. 5!
- Make a table with two columns showing what Mrs Blake and Shirley think about the Smiths.
- What kind of people could the Smiths in this play stand for? Explain!
- Describe Shirley's behaviour before and after she realizes that Miss Jones' companion is calle "Smith". (pp. 42+43) !
- What does Miss Smith mean when she says "after all, we are in England!! p. 45, l. 1)
- What is the effect of Mrs Blake's and Shirley's behaviour on the two women and on the audience? (pp. 43+44)?
Read the script of "An Incident" from the beginning to page 41, l. 34!
- If you were the producer of the play: What lighting and what sound would you suggest for the opening scene (p. 38, l. 1 to p. 39, l. 23)?
- Collect information and phrases that characterize Shirley, Miss Jones and Miss Smith. Start a separate sheet for each of the characters (This will be continued!)
- What are the problems and solutions mentioned in the video on this page
- Read this page on possible solutions for the problem of deforestation: Solutions
- Be prepared to present the content of this page in class!
- Watch this VIDEO and take notes!
- Be prepared to present the content of the video in class!
Look at the article and the short Statements on the American Dream today!
Add important aspects of what the dream means today and of what is criticised from our worksheet and the online-article! Start with/use the list below:
Basic ideas:
- All people are created equal
- Attitude of hope and faith fulfils your desire for success, prosperity, happiness, liberty, religious freedom
- Pursuit of happiness <= Declaration of independence
Different groups and dreams throughout history:
- Puritan pilgrim fathers: escape from Britain and religious freedom
- Settlers/pioneers: land, natural resources, personal freedom, abilities on your own hands work
- Revolutionaries/founding fathers: USA as the result of a successful revolution against the English king.
Democratic federal state! No nobility and no monarchy
- Immigrants in 19th and 20th century: new and safe life, escape from poverty, from prosecution, from inequality
Simple rules for those who want to live the dream:
- Work hard!
- Be patient, never give up!
- Believe in yourself and follow your dream!
- Believe in God and America!
- We can only do it together!
- If you want it, you can do it!
- You can be what you wanna be!
- Don´t dream it, do/be it!
- You get what you deserve!
Criticism / the dark side of the dream ...
- Working hard and wealth is over-emphasized. No time to enjoy what you have.
- Over-emphasizing material aspect oft he dream – spiritual and idealistic aspect is lost.
- Dream is unachievable for many people (poverty, inequality still exists).
- Dream gives a tough answer to those who don’t make it: „You didn’t try/work hard enough.
Describe and analyse this cartoon!
Joe Millionaire is an American reality television show that was broadcast on Fox beginning in January 2003.
The basic premise is that bachelor Evan Marriott has inherited millions of dollars and is searching for a potential bride. He takes a group of hopeful women on several dates to exotic and luxurious locations, eliminating women at the end of each episode until only one woman remains.
Aus https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joe_Millionaire
The Swan was a 2004 American reality television program broadcast on Fox. >br> Women who were judged to be ugly were given "extreme makeovers" that included several forms of plastic surgery. The title of the series refers to the fairy tale The Ugly Duckling, in which a homely bird matures into a swan.
Aus https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Swan_(TV_series)
Der Text für die Mediation liegt im Sekretartiat bereit ab 9.00 Uhr am Donnerstag, 3.3.2016!
Instructions:
- Read the text two times! Especially read the introduction!
- 1st reading: mark the relevant parts (according to what is specified in the introduction), also mark what is irrelevant (for addressee) and what are just examples etc.
- 2nd reading: write short keyword summaries/notes for each paragraph/relevant point. Identify repetitions, find similar points and finally reorder your notes/keywords! This will help you to write the mediation.
- Write your mediation! Don't forget the addressee/situation from the introduction. Write an appropriate introduction!
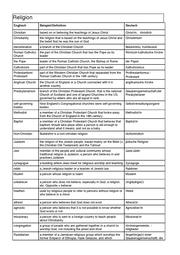
Book, p. 82/83 America is a religion
Answer Questions 18a+b on page 83! Answer part 18a in full, written sentences! Be prepared to explain 18b in class!
Describe and analyse this cartoon!
Write notes! I shall ask you to present it in class!
Finish the analysis of the cartoon!
The cartoon shows the effects of criticism of Islam and the islamic actions by religious leaders, politicions and the state. It is split up in four frames.
The solution can be found in the section on religion!
Von_Zuwanderern_lernen.zip Mediation herunterladen und mit Passwort entzippen!
Und wie gesagt: "Mediation ist ...! (Wer's Passwort vergessen hat: Mail an mich!)
Prepare a three minute talk on three negative effects of stereotypes:
Negative effects of stereotypes
(Cf. Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stereotype,
Stereotype threat
The effect of stereotype ....
Self-fulfilling prophecy
Stereotypes lead people to expect ....
Discrimination
Because stereotypes simplify and justify social reality, ...
- Write 3 different beginnings/introductorx paragraphs for a comment on:
- Mass immigration can still be a chance for Germany
- Explain (orally) what kind of comment will follow (structure …)
- Interprete this cartoon!
- ICE means: U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement
- Look at this information!!! before you start to describe the content and analyse the cartoon!
- Email your analysis to joerg.thelenberg@gmx.de by Wednesday, 28th October!
B) Watch the clip (perhaps you need to watch it two or three times)!
Questions (Take notes!) Be ready to present your answers to the whole course in a 3-4 minute talk!
- What is the EDL?
- What did Mr Robinson, the leader of the EDL, surprisingly do?
- What are the reactions from his former supporters and his muslim opponents?
- What does this divide mean for British society (in your opinion)?
A) Answer questions 2 and 3 on the worksheet!
B) Watch the clip from 0:00 to 1:25!
Questions (Take notes!)
- Who is interviewed?
- What is the question?
- What were his motives / are explanations for radicalization?
- Look at these statistics! and describe the situation of muslims in Britain on the basis of these data!
- If you are not sure how to work with statistics, see here!
- What effects does this have on the muslims' situation, attitudes and integration?
Just write down notes - NO FULLY WRITTEN OUT ANSWERS REQUIRED!
- Look at this information!!! before you start to describe the content of the cartoon!
- Describe the following cartoon (NOTES!)
Basic Skills & Information
- Information on homework and oral grades
- Reading and Marking technique - SQ3R Method A useful method to read, mark and annotate texts.
- Working with Cartoons
.
Muslims in Britain
Texts and Summaries
- A problem of perception: Muslims are well-integrated in Britain – but no one seems to believe it
- Problematic issues between British Muslims and the "Christian" majority
| fast-growing, disadvantaged part of population |
|
Situation:
Attitude:
|
Attitude:
Reasons:
|
Statistics
Statistics on muslims' education and emplyment!
- If you are not sure how to work with statistics, see here!
- What effects does this have on the muslims' situation, attitudes and integration?
Why do young muslims turn extremists?
- Read from beginning to "And it's a very powerful grip on one's mind. And in my case it took years to shed that influence." (third box)
Reasons for Extremism:
- crucial event: death of thousands of European muslims in war in Bosnia in 90s! West just watches and doesn't help the muslims there. (Parallels to wars in Iraq .... muslims are being killed and no-one cares)
- Islam is cleverly presented as way of looking at history: like in Marxism it is always a struggle, them against us, bad against good, everybody against the muslims (idea of Western/Jewish conspiracy against Islam/muslims)
- at school/in university young muslims become part of an active, organized, outspoken movement ⇒ proud to be an active muslim, feeling of power, feeling of belonging to group and of changing the world.
Cartoon
Cartoon women's rights in Islamic countries
.
Religion in the USA: The Christian Right, Megachurches and TV-Preachers
Vocabulary
.
Facts on Religion and Politics in the US
Special Religious Groups and Institutions
- (Evangelical) Mega-Churches
- church should not play the role of the state, but have clear positions
- against stem cell research
- against gay marriage
- against abortion
- some are liberal in enforcing their views
- 7,500 seats in church
- 11,000 congregants
Trends
- 72% of the Americans want their president to be clearly religious
- majority says churches should not endorse candidates
- half of the Americans think churches should express views on political matters
- 41% of the Americans want more religion in politics
- Americans are comfortable with showing their faith in public
- vote for candidates who aren't afraid to express their religious views
- only about 30% of Americans refuse gay marriage in 2003 - as compared to 41% in 1996
- about 25% are white evangelical christians and vote republican
- so many Americans believe that religion should not have any direct influence on and US politics but believe in religion being a privately exercised, individual matter
- many American Christians are not evangelicals and clearly want a more liberal, open-minded idea of Christianity and belief in God
Typical aspects/facts concerning religion in the USA
- US constitution strictly separates church and state
- US politicians - unlike their counterparts in Europe - often mention God in their speeches (God bless you, God bless America ...)
Influence of the Christian Right in the US
Cf. Book, p. 80/81
- Majority of conservative judges at US Courts appointed by Bush - hope for Religious Right?
- Religious Right fails at forcing schools to do school prayer and teach intelligent design.
- Religiously motivated influence on US Foreign Policy
- Most states forbid gay marriage while Washington refuses to include ban in Constitution
- Christian Right successful with ban on new stem cell research
- Supreme Court still rejects display of religious symbols in public institutions
TV-Preachers
.
Megachurches
Download Summary of facts about Osteen's megachurch
.
Cartoon
Cartoon ⇐Klick!
- 4 frames, three show acts of violence/hatred committed in the name of Christianity/Western Civilization
- evangelical pastor [=church] burning Korans, evangelical/conservative politician [politics] against building mosque in USA, secret service agent [=government] torturing terrorist suspect)
- irony: they all want revenge/act as unchristian/intolerantly as those they accuse of doing this to them
- irony: preacher is completely stupid: of course "them folks don't act like Christians" - they simply aren't christians!
- preacher also doesn't seem to know his Bilble: "Jesus hates Mohammed" is absolutely like anthing Jesus preaches in the Bible: Jesus preaches love, peace and forgiveness - not hatred!
- picture four shows the result: children in USA have learned, that you needn't act as you wish others to act towards you (in civilized way, mercyfully, helpfully, tolerantly ...) but can do anything you want as long as nobody stops you.
- General criticism: christian/western preachers and politicians and governments do the same things they accuse terrorists and radical islamist of ⇒ they are no better than them
Possible solution (full text):
Describe and analyse this cartoon!
Write notes! I shall ask you to present it in class!
Finish the analysis of the cartoon!
The cartoon shows the effects of criticism of Islam and the islamic actions by religious leaders, politicions and the state. It is split up in four frames.
In the first frame you can see a crazy older man, wearing a suit and tie, who publicly says „I’m burnin Korans ‚cause them folks don’t act like Christians.“and a sign in the background says „ Jesus hates Mohammed“. He represents the right winged Christians in the USA who strongly oppose Islam.
The second frame shows a TV where you can see a fat old angry man who thinks „We shouldn’t allow the Mosque in New York because they won’t allow Churches in Saudi Arabia.“ He refers to the mosque near Ground Zero in New York, which many Americans saw as an insult.
The third frame shows a man wearing dark suit and sunglasses and he`s holding something censored in his hand. He is interogating a suspect and is saying: "Its`s okay to torture terror suspects.`Cause they are utterly devoid of human decency."
In the last frame we can see a woman with three children sitting on the floor in front of her in a room with a big cross. She is trying to teach them the christian values, and begins a sentence: " And so, children we do unto others..."which a boy finishes with the words: " Any way we can get away with."
The cartoon criticizes the self-righteousness and hypocrisy of fundamentalist evangelicals, conservative politicians and the government that shows in their attitude to Islam and Muslims.
The pastor reveals not only his own limitations bey accusing the Muslims of not acting like Christians (which isn't really surprising for a Muslim) but shows his own hypocrisy or rather gross misunderstanding of what Jesus - who he claims hates Mohammed - teaches in the bible: tolerance, forgiveness, love and respect for orthers - not hatred and ar against them.
The politician seems only to have one motive - revenge for the way Saudi Arabia treats Cristianity, and he, too, reveals that he lacks a truly Christian, loving and forgiving attititude as well as a sound political strategy, that really helps Christians in the Arab world: The would rather profit from serious talks with Saudi Arabia (which is an ally of the US) and something like a political deal, that balances the mosque in New York with some churches in Saudi Arabia.
Basic Values: The American Dream, Puritanism and "God's Chosen people"
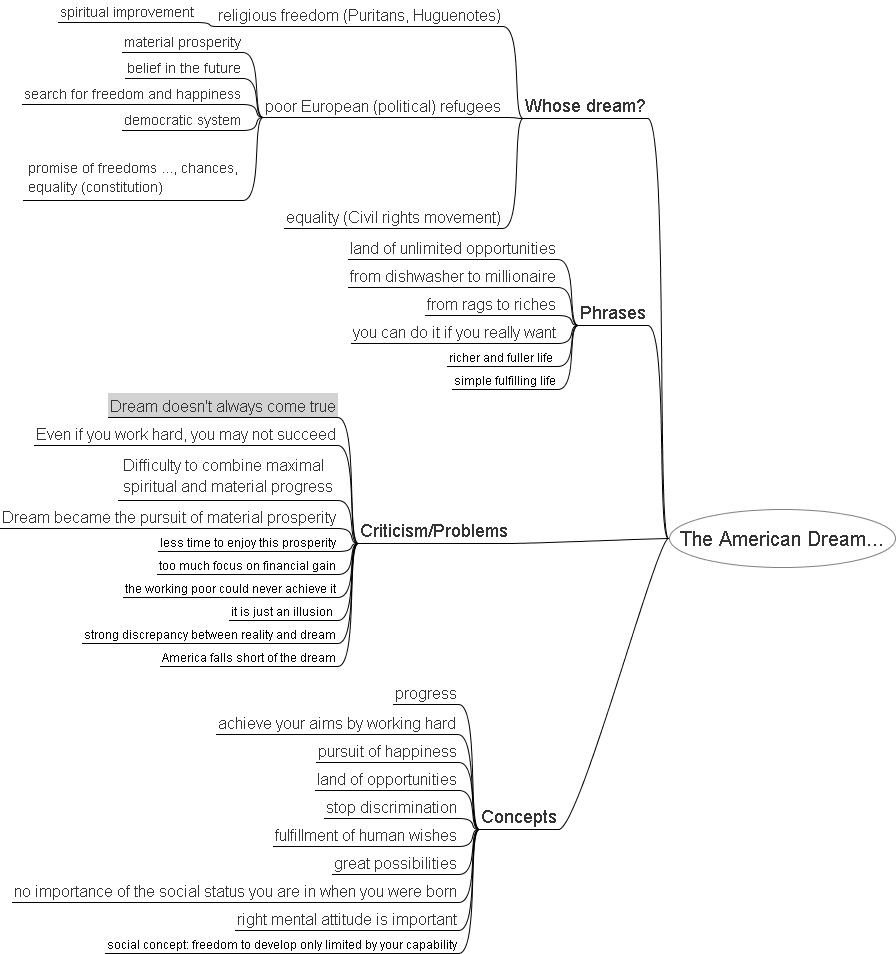
The American Dream
Links
- Cf. worksheet: "The American Dream Today"
- The American Dream (Wikipedia)
- Todaysamericandream.com
- Library of Congress: American Dreams
.
Explanation and Criticism
Basic ideas:
- Declaration of Independence:
- All men are created equal => everybody has the chance
- Pursuit of happiness
- Attitude of hope and faith
- fulfills your desire for success, prosperity, happiness, liberty, religious freedom
Different groups and dreams:
- Puritan pilgrim fathers: escape from Britain and religious freedom
- Settlers/pioneers: land, natural resources, personal freedom, abilities on your own hands work
- Revolutionaries/founding fathers: USA as the result of a successful revolution against the English king. Democratic federal state! => No nobility and no monarchy
- Immigrants: new and safe life, escape from poverty, from prosecution, from inequality
The American Dream is:
- to make money/have a job and to have a house
- to raise a family and care for them
- to build a better and safe future for you and your children through education, love, and hard work
- the right to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness, regardless of your skin color
- to be able to safely own the things you need or want
Rules/Guidelines
- Work hard!
- Be patient
- Never give up!
- Believe in yourself!
- Follow your dream!
- Believe in God and America!
- We can only do it together!
- If you want it you can do it!
- You can be what you wanna be!
- Don´t dream it, do/be it!
- You get what you deserve!
Criticism:
- Working hard and wealth is over-emphasized. No time to enjoy what you have.
- Over-emphasizing material aspect oft he dream – spiritual and idealistic aspect is lost.
- Dream is unachievable for many people (poverty, inequality still exists)
- The dream is a farce, a slogan used by politicians
- Many have no time for the American Dream, but are busy enough hanging on to what they have
- Dream gives a tough answer to those who don’t make it: „You didn’t try/work hard enough.
- Immigrants are widely held responsible for the failure of the American Dream
- Immigrants themselves are those who most ardently believe in the dream and see it fulfilled, as life is better than where they came from and will even be better for their children
.
Mindmap: The American Dream
.
Puritanism
Concepts of Puritanism in US Politics and Society
- Puritans in both Britain and British North America were part of a broad 16th century protest movement that showed a fierce passion to purge the established church and culture of what they regarded as corrupt, sinful practices. They fought against Roman Catholic ritual in church, against the ruling hierarchies, the ceremonies in which the clergy wore ornate vestments and repeated prayers from a prescribed liturgy and therefore had to leave England in the middle of the 16th century. New England’s Congregational churches were self-governed; worship services were simple and dominated by long, learned sermons in which their clergy (they elected their ministers!) explained passages from the Bible. As a result education, especially reading and writing, was seen as crucial for any good Christian, as without it one couldn't read the Bible, write sermons or prayers and understand religious teachings. .
- Puritans believed that the civil government should strictly enforce public morality by prohibiting vices like drunkenness, gambling, ostentatious dress, swearing, and Sabbath-breaking, and they believed in severe punishment for offenders. Accordingly, active, full membership in their churches was limited to the “visibly godly,” meaning those men and women who lead sober and upright lives. Also, like many Christians of this time, they believed that the devil finds work for idle hands. Therefore honest and hard work was seen as a virtue. .
- All Puritans shared the Calvinist belief in predestination – that God determined who would be saved or face damnation. Human beings were innately sinful by inheriting the original sin of Adam and Eve. But Calvin also taught that God would spare a small number of “elect” individuals from the fate of eternal hellfire. That elect group of “saints” would be blessed, at some point, and suddenly know that they possessed God’s “saving grace.” God had decided who would be saved or damned long ago, but even if good deeds and hard work couldn't result in being chosen, a life full of successful work, blameless behaviour and success status were clearly seen as visible proof of God's grace. Poverty, laziness, illness and a low status seemed, on the other hand, to show that one was not among the chosen ones. Another explanation is of course that by working hard, Puritans naturally often were successful, which then made them work even harder, as their success proved God's grace, which they had to be grateful for.
- The Puritan ideology was characterized by great hopes and the idea of predestination: they considered themselves God's chosen people with a singular sense of election, chosen to build a "New Jerusalem", "The City on the Hill" in the New World. Their advent on the world stage appeared in a sacred rather than secular light, it was to be grasped in terms of "meaning" and "destiny". So one vital contribution of the Puritan theology to American culture lies in the fact that it provided the settlers with an urge to create a "new order of the ages" (Novo ordis seclorum - the motto of the American seal). Soon Americans felt they had a "Manifest Destiny" to perform: to realize God's best plans, to set up a lighthouse for humiliated and oppressed man, to enlighten and civilize the rest of mankind. This messianic streak becomes evident in metaphors comparing America to a "Garden Eden" inhabited by the "New Adam".
- It also explains an outstanding sense of superiority and mission. Adding to this missionary zeal is a strong Manichean quality in Puritan religious thinking: the world tends to be considered in terms of good and evil, salvation and damnation. Thus there were (and are) spiritually and morally superior and inferior nations, a "Kingdom of Light" involved in an eternal struggle with the "Kingdom of Darkness", a struggle eventually to be decided in the apocalyptic Battle of Armageddon. Accordingly an amazing amount of self-righteousness, which luckily runs parallel to an equally amazing amount of public self-criticism can be considered a true characteristic of the American identity.
From (with adaptions): Christine Leigh Heyrman. Puritanism and Predestination. National Humanities Center <http://nationalhumanitiescenter.org/tserve/eighteen/ekeyinfo/puritan.htm>
Compare: America is a religion, book p. 82/82!
.
Immigration, Multiculturalism
Immigration
Immigration into Britain:
(Cf. book on page 50!)
Article on immigration from Eastern Europe
- history:
- Polish people immigrate to UK in increasing numbers from 2004 on - up to 700 000 - peak in 2007
- In 2009/10 numbers drop sharply … more Eastern European immigrants leaving than arriving
- reasons for coming:
- economic situation in East - jobs in Britain ==> comparatively few with high qualification ==> low skilled jobs
- reasons for leaving: less work in low-paid sectors of economy
- effects:
- massive demands for stop on immigration during peak of eastern European immigration
- * Polish immigrants are largest foreign group in Britain!
- * massive traces in everyday culture (e.g. food, churches …)
- Cf. handout about "Aspects of Immigration in Britain 2007" and "Maryam and her daughter Faith" about first and second generation immigrants!
.
Typical features in lives of immigrants in the USA - Buch 64/65 (Q 1):
(Cf. book p. 45)
- belief in American dream (job, house, provide for family)
- (parents) came to USA to have more opportunities/due to poverty in home country
- work
- first jobs in agriculture (fruit picking) or fast-food sector, textile industry
- children often have to work with parents
- often migrant workers
- often non-permanent, short-term employment
- low-paid jobs
- permanent resident or citizen status often through marriage with permanent resident or US citizen
- live simple lives, work hard, believe in American Dream
- often support other family members (in home countries)
- often not accepted/looked down upon by established/Caucasian US population
.
Immigrants as factor in US-elections
.
Cartoon on illegal immigration
- ICE means: U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement
Possible solution for interpretation of this cartoon:

.
Pros and cons of immigration
- http://www.embraceni.org/migration/the-pros-and-cons-of-migration/
- http://www.balancedpolitics.org/immigration.htm
| PROS of immigration | CONS of immigration |
|---|---|
|
|
.
Living together is difficult: Stereotypes
Definition
- ... are fixed, simple ideas or images that many people have of a particular type of person or thing
- ... often use simple criteria and give a simplified version of reality
- ... help us to categorize/distinguish between dangerous and harmless, attractive and unattractive, reliable - treacherous ...
- ... help us to understand and explain the world in a quick and simple way
- ... can be positive (men are strong) and negative (men don't have true feelings)
- ... are often very hard to change, even if experience suggests thtat the stereotype may be wrong/too simple to explain complex realties or individual behaviour
Effects of Stereotypes
(from Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stereotype,
Stereotype threat
The effect of stereotype threat (ST) on math test scores for girls and boys. Data from Osborne (2007).
Stereotype threat occurs when people are aware of a negative stereotype about their social group and experience anxiety or concern that they might confirm the stereotype. Stereotype threat has been shown to undermine performance in a variety of domains.
Claude M. Steele and Joshua Aronson conducted the first experiments showing that stereotype threat can depress intellectual performance on standardized tests. In one study, they found that black college students performed worse than white students on a verbal test when the task was framed as a measure of intelligence. When it was not presented in that manner, the performance gap narrowed. Subsequent experiments showed that framing the test as diagnostic of intellectual ability made black students more aware of negative stereotypes about their group, which in turn impaired their performance.
Stereotype threat effects have been demonstrated for an array of social groups in many different arenas, including not only academics but also sports, chess and business.
Self-fulfilling prophecy
Stereotypes lead people to expect certain actions from members of social groups. These stereotype-based expectations may lead to self-fulfilling prophecies, in which one's inaccurate expectations about a person's behavior, through social interaction, prompt that person to act in stereotype-consistent ways, thus confirming one's erroneous expectations and validating the stereotype.
Word, Zanna, and Cooper (1974) demonstrated the effects of stereotypes in the context of a job interview. White participants interviewed black and white subjects who, prior to the experiments, had been trained to act in a standardized manner. Analysis of the videotaped interviews showed that black job applicants were treated differently: They received shorter amounts of interview time and less eye contact; interviewers made more speech errors (e.g., stutters, sentence incompletions, incoherent sounds) and physically distanced themselves from black applicants. In a second experiment, trained interviewers were instructed to treat applicants, all of whom were white, like the whites or blacks had been treated in the first experiment. As a result, applicants treated like the blacks of the first experiment behaved in a more nervous manner and received more negative performance ratings than interviewees receiving the treatment previously afforded to whites.
A 1977 study by Snyder, Tanke, and Berscheid found a similar pattern in social interactions between men and women. Male undergraduate students were asked to talk to female undergraduates, whom they believed to be physically attractive or unattractive, on the phone. The conversations were taped and analysis showed that men who thought that they were talking to an attractive woman communicated in a more positive and friendlier manner than men who believed that they were talking to unattractive women. This altered the women's behavior: Female subjects who, unknowingly to them, were perceived to be physically attractive behaved in a friendly, likeable, and sociable manner in comparison with subjects who were regarded as unattractive.
Discrimination
Because stereotypes simplify and justify social reality, they have potentially powerful effects on how people perceive and treat one another. As a result, stereotypes can lead to discrimination in labor markets and other domains. For example, Tilcsik (2011) has found that employers who seek job applicants with stereotypically male heterosexual traits are particularly likely to engage in discrimination against gay men, suggesting that discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation is partly rooted in specific stereotypes and that these stereotypes loom large in many labor markets.[14] Agerström and Rooth (2011) showed that automatic obesity stereotypes captured by the Implicit Association Test can predict real hiring discrimination against the obese.[74] Similarly, experiments suggest that gender stereotypes play an important role in judgments that affect hiring decisions.
Stereotypes against Asian Americans
What stereotypes about Asian Americans are there? Make a structured list (sex, positive/negative ...)
- Men
- + clever, hard working
- + technology-freaks, good with computers
- - nerds
- - not masculine/effeminate
- - not athletic
- - short
- Women
- + exotic (sexually attractive)
- + clever, hard working
- + submissive/demure
- - too clever(for many men), tricky
... against African Americans
Positive or negative ..? - what effects?
... against Hispanic/Latino Americans
Positive or negative ..? - what effects?
.
Concepts of living together
Cf. worksheet "Concepts for diverse societies"
- multiculticulturalism - ethnic diversity
- salad bowl
- American quilt
- American mosaic/kaleidoscope
- American pizza
- cultural assimilation
- melting pot
- complete Americanization
Multiculturalism - Does it work?
- Book p. 51
- Multiculturalism is a failure as it leads to segregation and lack of assimilation into British culture
- Ghettoization and lack of intermarriage speak a clear language ⇒ no assimilation of some ethic groups
- Criticism of multiculturalism is not not racism, but an expression of the mainstream culture's efforts to defend against all otherness
- Not only immigrants, but all groups and classes live and socialize preferrably with people of a similar social type
- Most Britons think: Not mixing is okay as long as it doesn't threaten society, as long as general acceptance of British laws and culture is not in danger
.
Who we are - who we want to be: Obesity, Good Looks and Plastic Surgery
Obesity
Reasons for obesity:
- medical/biological disposition or use of medication (rare)
- unhealthy food cheaper than healthy food
- too much salt, sugar and fat
- people eat a lot of sugar without knowing
- sugar increases your appetite
- cornfructose is a very cheap + good tasting ingredient
- labels like smart choice make things worse, as they make people eat more and as they advertise fat free food, but fat is replaced by sugar
- we do not only eat when we are hungry
- we do not think about how much and what we eat
- marketing of cheap / high-calorie/sugary food and extremely large portions
- insufficient physical exercise compared to amount of food we eat
Effects of obesity:
- high cholesterol + and blood-sugar ==> heart diseases, diabetes, stroke,
- various cancers, massive diabetes
- problems with joints (knees, ankles, hips) due to massive overweight
- reduced life-expectancy
- health care costs and costs of unemployment, long-term-illnes and care for extremely obese people increase dramatically
- problems with public transport, travel, etc. => loss of mobility
- severe limitations / loss of quality of life => depression, isolation
Possible solutions:
- more exercise/sports
- eat more low calorie food
- legal steps against hidden sugar, oversize portions, … for better information on labels of food we buy
- instruct kids in school + change school lunch
- teach people about consequences and responsible eating (portion sizes, sugar intake, ...)
- make children walk to school instead of going by bus
- local restaurants can change their menus + portion sizes
- drink less beer and high-sugar softdrinks
.
Good looks
How much do looks count today? (Cf. worksheet/handout)
The cult of youth, beauty and the body:
.
Plastic surgery
Statistics
.
Videos
Plastic surgery for teenagers
Plastic surgery for men
Reasons for plastic surgery
Plastic Surgery for Women:
Text: Cultural Obsession with Youth and Beauty
- to look like the women in the media
- everybody does it (celebrities, models, mothers, sisters, aunts, ...)
- prices go down
- it feels good to get told that you look good
- to improve their self-confidence
- to remind themselves of the good times (when they were younger, fitter, more attractive ...)
- people don´t like themselves because they are brainwashed by the media
- to be more attractive for men
- to have better job chances
- youth shows fertility
- to wear the newest dresses ( fashion )
Plastic Surgery for Men:
- want to have more success in jobs
- want to attract younger women
- want to emit an image of vitality
- makes them feel better
- to look more attractive
- to get attention from other people
- to look young, fit, with good reactions and professional
- to bring out their (male, youtful) character
- to prevent prejudice (e.g. against obese, old, unsporty people)
.
Mediation on plastic surgery for men
- Textvorlage unter Die Sehnsucht der Männer nach dem perfekten Körper
- Introduction:
- A friend of yours who lives in the US is writing a report on plastic surgery as a growing international trend.
- As he doesn't speak German he has asked you to give him some information about the reasons for especially men to undergo plastic surgery and the problems that this can cause.
Possible content:
Introduction - addressing friend ... There are several reasons for men to choose plastic surgery:
Possible medical reason (rare)
- removal of cells responsible for extensive sweating
Usual reasons:
- men want to look younger
- want to feel satisfied/happy/confident with their own body
- want to become and stay slim without constant dieting or sports, which reduce theit quality of life or cost much time and effort
- increased job competition among peers and with younger generation: physical fitness/good looks are linked to leadership qualities
- advertising and changing values in society exert pressure on men to come close to the male ideal of beauty
- today men have more time and are more encouraged to ponder and care about whether they are beautiful and develp a body cult
But there are clear problems, too
- belief that better looks directly result in better job chances or solve personal problemsè wrong motivation for plastic surgery
- men undergo extensive plastic surgery even if they do it for the wrong reasons or are psychically instable
- (there are plastic surgeons who accept patients that are to labile)
- it is difficult for patients to ensure that their doctor is qualified, as "plastic surgeon" is not a legally definable qualification
- patients oft want too much in a very short time è increased medical risks
- many men are not sufficiently informed or want to really consider possible problems
- medical riscs of operation (complications, medical malpractice, infection, dissatisfying results)
- men feel that their plastic surgery must be kept a secret => avoid envy (patient can afford high costs!), being accused of cheating/giving in to ideals of beauty
Environment
Vocab
| deforestation | Abholzung |
| to fell sth. | etw. fällen |
| to dispose of sth. | etw. beseitigen |
| to liquidate | beseitigen |
| logger | Holzfäller |
| logging | Holzgewinnung |
| slash-and-burn | Brandrodung |
| clear-cutting | Kahlschlag |
| agricultural areas | Landwirtschaftliche Flächen |
| arable land | Ackerfläche/ bebaubares Land |
| habitat | Lebensraum |
| acreage | Ackerland |
| grazing land | Weideland |
| swaths | Schneise |
| remote forests | abgeschiedene Wälder |
| plantation | Plantage |
| crop / plant | die Pflanze |
| forestry | die Forstwirtschaft |
| land use | die Landnutzung |
| cultivation | die Bewirtschaftung |
| rainforest | der Regenwald |
| reasons for deforestation | Gründe für Abholzung |
| anthropogenic | vom Menschen verursacht |
| insatiable demand | unersättliche Nachfrage |
| subsistence | Eigenbedarf |
| timber industry | Holzwirtschaft |
| fuel wood | Brennholz |
| soy industry | Sojaindustrie |
| hydroelectric project
hydroelectric power station |
Wasserkraftprojekt
Wasserkraftwerk |
| mining operation | Bergbaubetrieb |
| soy | das Soja |
| sugar cane | das Zuckerrohr |
| palm oil | das Palmöl |
| biofuel | der Biotreibstoff/-kraftstoff |
| consequences | Folge |
| scarcity | Knappheit |
| biodiversity | Artenvielfalt |
| extinction | Auslöschung / Ausrottung / Aussterben |
| vulnerable species | gefährdete Gattungen |
| erosion | Erosion |
| barren soil | unfruchtbarer, dürrer Boden |
| devastating
devastated |
Verwüstung
verwüstet |
| declining harvest | abnehmende Ernte |
| overgrazing | Überweidung |
| eviction | Vertreibung |
| encroachment of land | Beeinträchtigung von / Übergriff auf |
| depletion of the woods/soil | Ausdünnung der Wälder, Erschöpfung des … |
| impoverishment
impoverished |
Verarmung
verarmt |
| global warming | die Erderwärmung |
| emission | die Emission |
| climate change | der Klimawandel |
| carbon dioxide / monoxide | das Kohlendioxid/ -monoxid |
| to release sth. into | etwas freisetzen in ... |
| (over) exploitation | der Raubbau |
| destruction | die Zerstörung |
| solutions | Lösungen |
| planting
to plant |
Bepflanzung
pflanzen |
| drive demand down | Die Nachfrage verringern |
| to provide valuable ecosystem services | Dem Ökosystem wertvolle Dienste leisten |
| government moratorium | Baustopp der Regierung |
| recruitment of | Anwerbung von |
| reforestation | Wiederbewaldung/Wiederaufforstung |
| to restore | wiederherstellen |
| to preserve | aufrechterhalten / bewahren |
| preservation | der Erhalt |
| to regrow | wieder wachsen (lassen) |
| to sequester interest groups/ stakeholders | Interessensgruppen/ Teilhaber absondern |
| sustainable consumption | nachhaltiger Konsum |
| topic area: "Deforestation for cheap meat in Europe" | Themenfeld: "Abholzung für billiges Fleisch in Europa" |
| feed | Mastfutter |
| feedstuff | Futtermittel |
| poultry | Geflügel |
| commodity | Handelsgut |
| yield | Ertrag |
| boycott-campaign | die Boykott-Kampagne |
| others | Sonstiges |
| pesticides | Pflanzenschutzmittel |
| herbicides | Unkrautbekämpfungsmittel |
| canopy | Baumkrone/ Blätterdach |
| indigenous | einheimisch |
| rural | ländlich |
| environment | die Umwelt |
| environmentalist | der Umweltschützer |
| climate protection measure | die Klimaschutzmaßnahme |
| protection | der Schutz |
| energy conservation | das Energiesparen |
| to counteract sth | etw. entgegenwirken |
Facts, Causes, Effects and Solutions
Environmental DOs and DON'Ts
Zum Vergrößern mehrfach klicken und dann speichern ...!
.
Interview questions
Deforestation
- Do you support organisations against deforestation?
- Which are the main causes of deforstation?
- What are the consequences if we do not stop deforestation?
- Which area of forest is cut down daily?
- What are possible solutions for stopping deforestation?
- Are we guilty ?
- What do you know about deforestation?
- What are the consequences of deforestation?
- Why are people cutting down so many trees?
- What will happen all over the world if deforestation won't stop?
- What can each person do to stop deforestation?
- Are there any companies/organi which are trying to stop deforestation
- What's your first intention when you think of 'deforestation' ?
- Would you support deforestation in Germany ?
- Dou you think that our forests need to be protected ?
- Can you imagine the consequences of the deforestation of the rainforest ? #Murica
- Is it just a local problem or even a global one?
- What do you know about deforestation?
- How does deforestation affect you?
- Are you actively against deforestation?
- Do you use rare kinds of wood which could be from the rainforest?
- Where does deforestation happen?
- Do you think that deforestation will affect your life in the next 10 years?
- Would you donate money to an organisation which fights against deforestation?
- Is deforestation in Germany worse than in Russia and eastern european countries?
- Do you think deforestation is necessary?
- Where is deforestation causing the most problems?
- What is deforestation?
- What is the extend of the problem?
- Is deforestation occurring within the eu?
- What are the causes of deforestation?
- How can we stop deforestation?
- Why are my questions so short?
- Why does deforestation happen?
- How does it affect us?
- Where does it happen?
- Will it kill us in the long run?
- What companies make profits from deforestation?
- Why should people stop deforestation?
- Do people demonstrate against deforestation?
- How could deforestation influence your life?
- Where is deforestation a big problem?
- How can we stop it?
- Do you know negative consequences of deforestation?
- How can you improve the situation?
- What do you think about deforestation?
- Are there any organisations against deforestation?
- Where does deforestation happen?
- Why is it a problem?
- How does it happen?
- Does it affect everybody?
What is our part in all this? Do you like cheap meat?
- What problems are mentioned? Who/what is affected?
- Who is responsible? (directly and indirectly?)
- What solutions are there?
Summary on "Cheap meat for Europe"
What problems are mentioned? Who/what is affected?
In order to meet costumers' expectations new ways of producing inexpensive meat had to be found but this also causes many problems.
First of all the indigenous people, e.g. in Paraguay, have been forced to give away their land. This represents a violation of basic human rights. But these people harldy have a chance to fight back as they are brutally threatenend by police and paramilitary units.
In addition, the forests, having so far provided the locals with animals or fruits, are cut down. Thousands of square miles of forest has already been destroyed and millions of trees have been cut to make way for soy plantations.
Even more worrisome for the indigenous people is the usage of pesticides. They risk of diseases like diarrhea or genetic malformations, just to mention a few, is very high. The damage which has already been done to nature can't be repaired. So far, rivers and lakes have been polluted by billions of tons of poisonous substances.
Another offense against human dignity is the fact that a lot of the locals are driven to urban areas where they end up in slums and poverty. Besides they learn that they live in a country where corruption is widespread and where environmental regulations are so poor that companies can easily occupy their land.
Who is responsible?
Among the various countries which are supplied with animal feed it is China, which needs the largest quantity of it. It is followed by European countries like Germany, Italy and the Netherlands. These countries have turned to soy as a consequence of the BSE crisis.
What solutions are there?
A number of people all over the world have understood the problems poor countries have to face. They want to find solutions to protect the forests and the indigenous communities. They consider introducing new laws to help not only nature but also the native residents. Furthermore they are trying to find to find an alternatives to soy (like sweet lupins, that are grown in Europe and are excellent cattleffed and help to improve the soil) as 97% of soy is used for animal feed. It's very important to raise awareness among consumers of cheap meat. If they they go on buying these products our environment will be effected badly. Above all, the human rights of the indigenous people will still be disregarded.
.
Cartoons
.
http://no2deforestation.wordpress.com/ http://no2deforestation.wordpress.com/
Drama, Baby, Drama
From Poetry to Drama
Watch the difference between poetry and drama:
To turn the recital of a poem into "drama" one must/should ...
- put emotion in by varying the level of your voice
- vary your speed, speak in a shivering/slow/tired voice
- use gestures and facial expressions
- introduce music to support the mood e.g. slow instrumental piece
- e.g have several actors, representing the victims and the police. The victims are taken away one after the other. One person recites the poem.
- create interaction between characters e.g. others passivly watch
- use costumes e.g. for the soldiers, police, servants, different classes
- use images as background
- use a chorus, which speaks certain passages together
- not do any of these to keep it minimalistic
- use lighting e.g. spot on one actor
.
Voice and the characters' interaction change everything!
... or can at least almost completely change the effect of the same line.
- Compare these examples!
- Practice this sentence with a partner (Take turns, play at least two different versions, the silent partner uses gesture/facial expressions)!
- I don't know what what she's up to. I just want to say "Good-bye".
- What is the general situation? (When, where does this happen?)
- What is the relation between the two characters (Who are they?)
- What do the characters want to express? (verbally and non-verbally)
.
Drama - a Definition
Drama is the specific mode of fiction represented in performance. The term comes from a Greek word meaning "action" (Classical Greek: δρᾶμα, drama), which is derived from "to do" (Classical Greek: δράω, drao). The enactment of drama in theatre, performed by actors on a stage before an audience, presupposes collaborative modes of production and a collective form of reception. The structure of dramatic texts is directly influenced by this collaborative production and collective reception. From http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drama
.
Fiction: Food for all his Dead
Characterization
Example for indirect characterization
In the text one can find several examples of indirect characterization.
This becomes clear in line 38 to 40, where Jonny’s father tells his son to make money and help the people in his district. This allows the reader to draw the conclusion, that the old man is conservative and wants his son to be a respected member of the Chinese society. [<= example 1]
… [example 2] …
So the characterization is not achieved by the narrator telling the audience about the characters but by showing them in what they say and do.
Facts for characterization of Johnny and his father
| Johnny
|
Johnny's father
|
.
Introductory sentence
Johnny and his father are in many ways different. While his father shares traditional Chinese values, Johnny is a young open-minded Americanized teen.
While Johnny … his father …
In contrast to Johnny, his father>br>
Johnny …, but his father …
.
Question 4: Who is responsible for Johnny's problem?
Johnny´s problems:
- doesn´t want to be Chinese
- doesn´t want to live up to his father´s expectations
- wants to be himself → leave Chinatown
- can´t live the way he wants to live
- doesn´t share his family´s values
- he doesn´t know who he is
- has his identity, safety and confidence, which he was sure of as a child
Who is responsible:
- American lifestyle/world around him (influences his views and attitude, society, media, friends, school, lang.)
- father ( bringing him to America, sending him to an American school, pressurizing him to be successful in the A. system)
- => cruel irony: father himself caused the estrangement between his son and himself.
The right to bear arms … - a basic value?
The Second Amendment to the US Constitution
The right to keep and bear arms in the United States is a fundamental right protected by the Second Amendment to the United States Constitution, part of the Bill of Rights, and by the constitutions of most U.S. states.
The Second Amendment declares:
„A well regulated Militia, being necessary to the security of a free state, the right of the people to keep and bear Arms, shall not be infringed.“
Federal Court Commentary
Supreme Court justice Antonin Scalia in 2008 wrote that the right to bear arms is not unlimited and is subject to reasonable prohibitions and regulations and subsequently federal court rulings have upheld existing gun prohibitions and regulations.[57] Nadine Strossen, former president of the American Civil Liberties Union, has stated that the individual rights model must yield to reasonable regulation.[58] Strossen said "it is no more absolute than freedom of speech or any other right in the Constitution. No right is absolute; the government is always allowed to restrict the right if it can satisfy Constitutional strict scrutiny and show the restriction is narrowly tailored to promote a goal of compelling importance."[59]
Research: Problems and solution tot he gun crisis?
Read the three articles (1 per team) and write an clear outline of he facts that help to answer these three questions:
- What is the scale and true nature of America’s gun problem?
- Where are gun rights supporters right – and the media are wrong?
- What measures do work – and what measures don’t?
Gun Control - Pro and Con