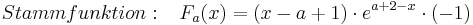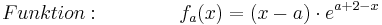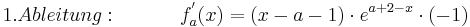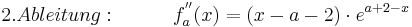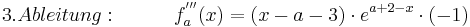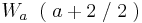Lösungsübersicht: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Aus RMG-Wiki
(→Teilaufgabe d)) |
(→Funktion) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
== Funktion == | == Funktion == | ||
| − | + | :<math>Stammfunktion: \;\;\; F_a (x) = ( x - a + 1 )\cdot e^{a + 2 - x}\cdot (-1) </math> <br /> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | :<math>Funktion: \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; f_a (x) = ( x - a )\cdot e^{a + 2 - x} </math> <br /> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | :<math>1. Ableitung: \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \;\;\; f^{'}_a (x) = ( x - a - 1 )\cdot e^{a + 2 - x}\cdot (-1) </math> <br /> | |
| + | |||
| + | :<math>2. Ableitung: \;\;\;\; \;\;\;\;\;\;f^{''}_a (x) = ( x - a - 2 )\cdot e^{a + 2 - x} </math> <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>3. Ableitung: \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; f^{'''}_a (x) = ( x - a - 3 )\cdot e^{a + 2 - x}\cdot (-1) </math> <br /> | ||
=== Teilaufgabe a) === | === Teilaufgabe a) === | ||
Version vom 22. Januar 2010, 01:23 Uhr
Inhaltsverzeichnis |
Funktion
Teilaufgabe a)
Nullstelle:
Schnittpunkt mit der y-Achse:
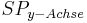
Extrempunkt:
Wendepunkt:
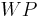
Funktionsgleichung aller Extrempunkte:
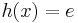
Teilaufgabe b)
1. Fürist der GFa streng monoton fallend.
Fürist der GFa streng monoton steigend.
Fürbesitzt GFa eine Tiefpunkt.
2. Stammfunktion: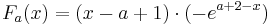
3. Flächeninhalt zwischen der x-Achse und dem Graphen der Funktion f2: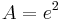
Teilaufgabe c)
1.2.
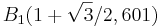
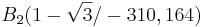
Teilaufgabe d)
1.
Da sich die y-Werte dieser Punkte nicht verändern, haben diese immer denselben Abstand
zueinander. Deshalb sind alle Dreiecke, die durch diese Punkte festgelegt sind, kongruent. 2.